Different Types Of Airbags In Cars – Feature Explained
Airbags are a critical safety component in modern cars and SUVs, designed to minimise injuries in the event of a collision. They work in conjunction with seatbelts to provide a cushion, reducing the impact force on occupants. Over the years, airbag technology has evolved significantly, leading to the development of various types of airbags that offer enhanced protection in different crash scenarios.

Let’s take a closer look at the different types of airbags in cars and how they work so you can make an informed decision while buying your next car.
1. Front Driver And Co-Passenger Airbags
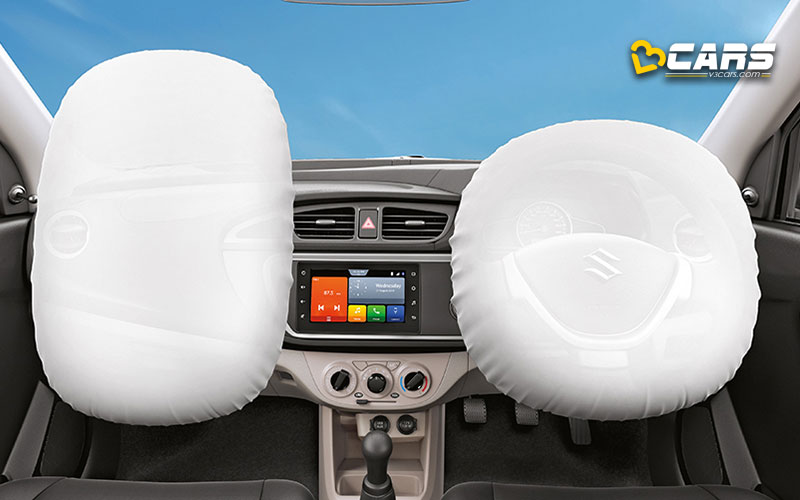

These are the most common type of airbags. Front driver and co-passenger airbags. All new cars sold in India since April 1, 2021 come with front driver and co-passenger airbags as standard.
How they work:
- Located in the steering wheel hub (for the driver) and the dashboard (for the front passenger).
- In a frontal collision, sensors detect the sudden deceleration and send a signal to the airbag inflator.
- The inflator rapidly fills the airbag with gas (typically nitrogen or argon) within milliseconds.
- The inflated airbag cushions the head and chest, preventing them from hitting the steering wheel, dashboard, or windshield.
- The airbag then deflates quickly to allow the occupant to move and prevent suffocation.
Pros:
- Front driver and co-passenger airbags are effective in reducing injuries in frontal collisions, which are among the most common and dangerous types of car accidents.
- Significantly decreases the risk of serious head and chest injuries.
- Now a mandatory safety feature in India.
Cons:
- Not effective in side-impact, rear-end, or rollover accidents.
- Can cause minor injuries (abrasions, burns) due to the force of deployment.
- Improper use (e.g., sitting too close to the airbag) can increase the risk of injury.
2. Front Side Airbags
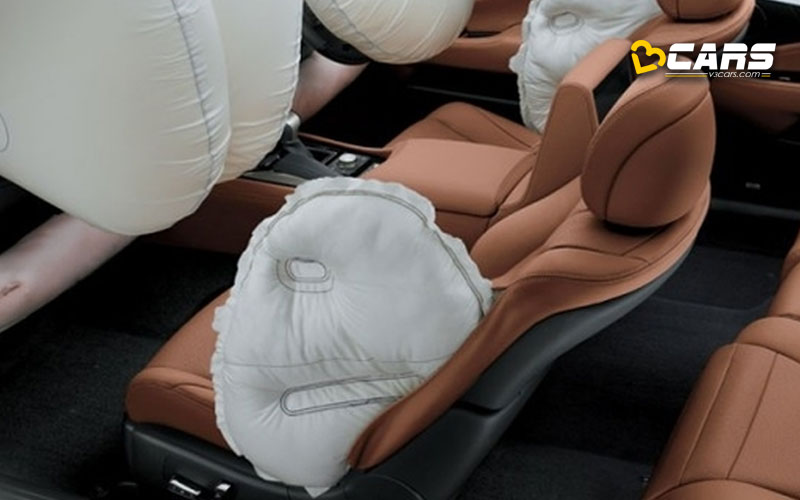

Front side airbags airbags are designed to protect the torso (chest and abdomen) in side-impact collisions.
How they work:
- Typically located in the side of the seatback or the door panel.
- Side-impact sensors detect a collision and trigger the airbag on the affected side.
- The airbag inflates outwards, creating a cushion between the occupant’s torso and the intruding structure (door, side of another vehicle).
Pros:
- Greatly reduces the risk of chest and abdominal injuries in side-impact crashes, which can be very severe.
- Works in conjunction with the car’s side structure to absorb impact energy.
Cons:
- Offers limited protection for the head and extremities.
- Deployment can sometimes cause minor injuries.
- May not be as effective in angled side impacts.
3. Side Curtain Airbags
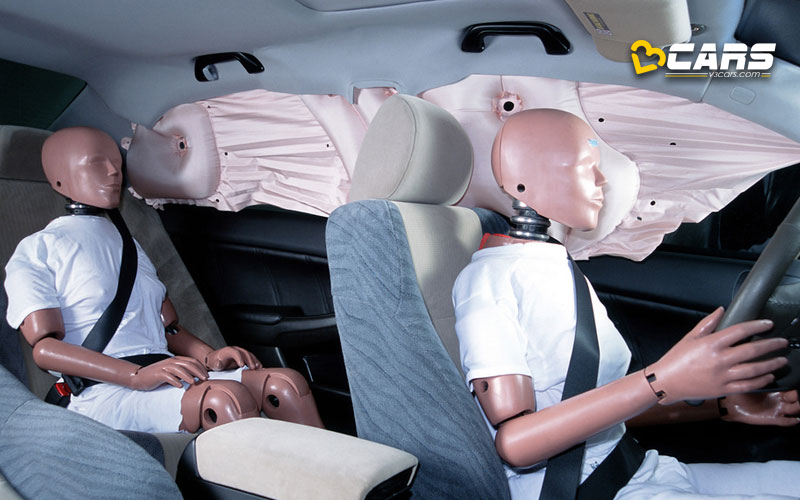

Also known as “roof airbags” or “overhead airbags,” side curtain airbags provide head protection in side-impact collisions and rollovers.
How they work:
- Located in the headliner (the fabric lining the car’s roof) above the side windows.
- In a side-impact or rollover, sensors trigger the airbag to deploy downwards from the roof.
- The airbag forms a protective curtain that covers the side windows, cushioning the head and preventing it from hitting the side pillars, window glass, or objects outside the car.
- In a rollover, the curtain airbag can remain inflated for a longer period, offering continued protection.
Pros:
- Excellent protection against head injuries in side-impacts, especially in collisions with tall vehicles or objects.
- Provides crucial head protection in rollover accidents, which have a high risk of severe injury.
- Protects both front and rear occupants.
Cons:
- Offers no protection for the torso or extremities.
- Deployment can sometimes cause minor injuries.
4. Knee Airbags
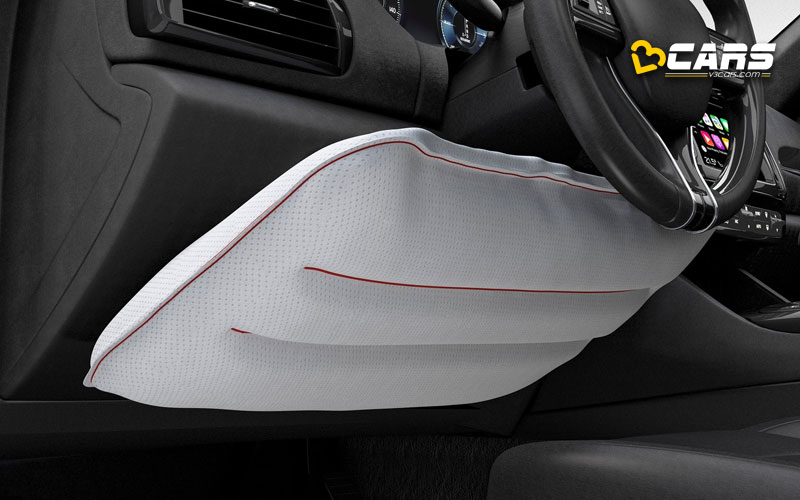

These airbags are designed to protect the driver’s and/or front passenger’s knees and lower legs.
How they work:
- Located in the lower part of the dashboard, below the steering column or glove compartment.
- In a frontal collision, sensors deploy the knee airbag.
- The airbag inflates and cushions the knees and lower legs, preventing them from hitting the dashboard or being forced into the footwell.
Pros:
- Reduces the risk of knee, femur (thigh bone), and lower leg injuries.
- Helps to position the occupant correctly in the seat, maximising the effectiveness of the front airbags.
Cons:
- Offers no protection to the upper body or head.
- Their effectiveness can be reduced if the occupant is not wearing a seatbelt.
5. Seat Cushion Airbags
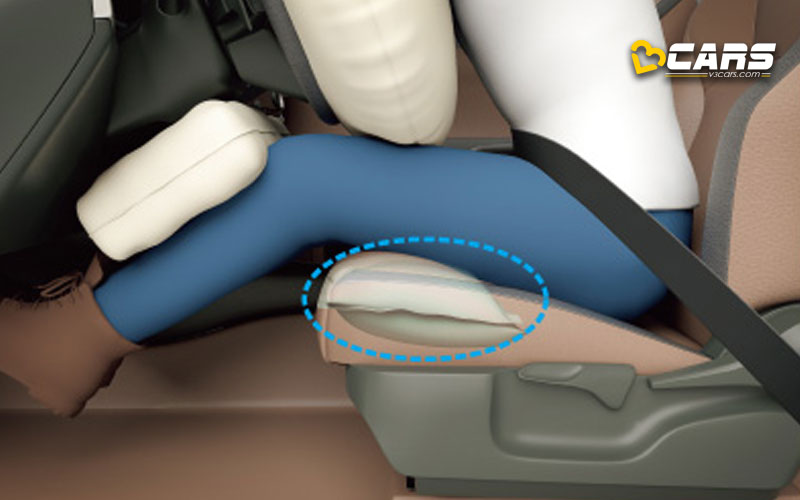
These are less common but are designed to prevent “submarining,” which is when an occupant slides underneath the seatbelt in a frontal collision.
How they work:
- Integrated into the seat cushion.
- In a frontal collision, the airbag inflates upwards, raising the front edge of the seat.
- This helps to keep the occupant’s pelvis in the correct position and prevents them from sliding forward under the lap belt.
Pros:
- Effective in reducing the risk of submarining, which can cause serious abdominal and spinal injuries.
- Improves the effectiveness of the seatbelt.
Cons:
- More complex and expensive to implement than other types of airbags.
6. Seatbelt Airbag

Seatbelt airbags are designed to provide additional protection to passengers in frontal collisions. This type of airbag inflates to distribute the force of the impact over a larger area of the body.
How they work:
- Seatbelt airbags are integrated into the seatbelt webbing.
- In a front collision, the airbag inflates within the seatbelt, thus increasing its surface area.
- The increased surface are reduces pressure on the chest and shoulders, minimising the risk of injury.
Pros:
- They are effective in reducing chest and shoulder injuries.
- Provides better support than standard seatbelts.
- Works in conjunction with other airbag systems for enhanced safety.
Cons:
- More complex and expensive than standard seatbelts.
- May be uncomfortable for some users.
- Not as effective in side-impact or rollover accidents.
Can Airbags Be Fitted Aftermarket In India?
While it’s technically possible to install some types of airbags aftermarket, it’s generally not recommended in India, and here’s why:
- Complexity: Integrating airbags into a car’s existing safety system is extremely complex. It requires precise sensor placement, wiring, and compatibility with the car’s electronic control unit (ECU).
- Reliability: Aftermarket installations may not be as reliable as factory-installed systems. Improper installation can lead to airbag malfunction, either failing to deploy in a crash or deploying at the wrong time.
- Safety Risk: A malfunctioning airbag can cause serious injury or even death.
- Cost: A proper aftermarket installation, if done by a qualified professional, can be very expensive.
- Warranty Issues: Installing aftermarket airbags can void the car’s warranty.
- Legal Complications: In some cases, modifying a car’s safety system may not be legal or may affect insurance coverage.
Airbags have revolutionised car safety, significantly reducing the risk of severe injuries and fatalities in accidents. From the basic front airbags to more advanced side, curtain, knee, and seat cushion airbags, each type plays a crucial role in providing comprehensive protection. While aftermarket installation might seem like an option, the risks and complexities involved make it highly inadvisable. It’s always best to choose a car with a complete set of factory-installed airbags to ensure optimal safety.
Affordable Cars In India With 6 Airbags
Here’s a list of cars priced under Rs. 10 lakh (ex-showroom) that offer 6 airbags as standard:
- Maruti Suzuki Alto K10
- Maruti Suzuki Celerio
- Maruti Suzuki Baleno
- Toyota Glanza
- Maruti Suzuki Brezza
- Maruti Suzuki Fronx
- Kia Syros
- Citroen Aircross
- Citroen Basalt
- Honda Amaze
- Tata Nexon
- Kia Sonet
- Mahindra XUV 3XO
- Hyundai Venue
- Skoda Kylaq
- Hyundai i20
- Maruti Suzuki Dzire
- Maruti Suzuki Swift
- Hyundai Aura
- Citroen C3
- Nissan Magnite
- Hyundai Exter
- Hyundai Grand i10 Nios
- Maruti Suzuki WagonR
- Maruti Suzuki Eeco
Note: Check your Car EMI with our - Car Loan EMI Calculator
You can use our Fuel Cost Calculator to see how much any petrol, diesel or CNG car will cost to run based on the latest fuel price in your city.


0 Comments